Introduction to Natural Systems
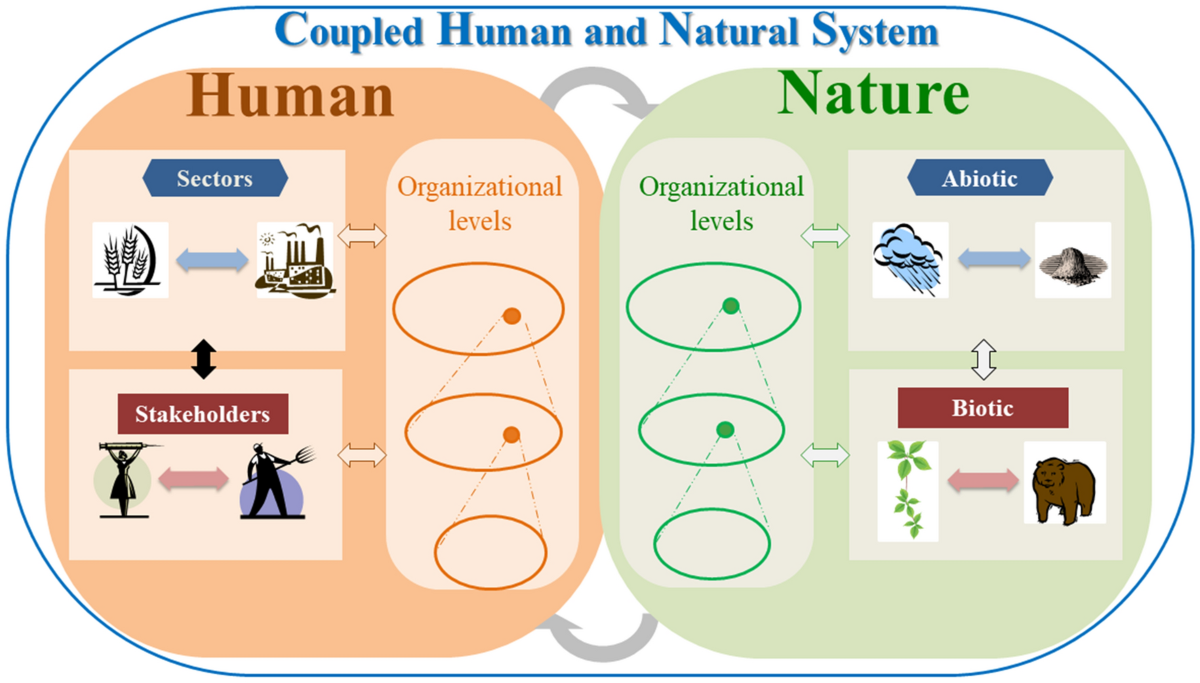
Natural System in Use refer to the complex networks of physical, chemical, and biological processes that occur in nature. These systems can be defined as interrelated components that function cohesively to maintain ecological balance. They encompass a wide range of environments, from biomes like forests and oceans to individual elements such as ecosystems and habitats. Understanding the characteristics of natural systems is crucial to recognizing their significance in our world.
A fundamental principle governing Natural System in Use is the concept of interdependence. In these systems, every element has a role, contributing to the overall stability and sustainability of the environment. For instance, producers, such as plants, convert sunlight into energy, which supports primary consumers, like herbivores, and then flows through to secondary consumers, such as carnivores, creating complex food webs. Furthermore, natural systems are characterized by feedback loops, in which the output of a process influences its own operation, thereby maintaining equilibrium within the environment.
The relevance of Natural System in Use extends beyond ecology; they play a pivotal role in the maintenance of air and water quality, nutrient cycling, and biodiversity. These elements are crucial in sustaining life on Earth, making their understanding integral to addressing environmental challenges. By studying the interactions within these systems, researchers and policymakers can cultivate strategies that align with the natural system in use, ensuring a sustainable future.
In essence, Natural System in Use are indispensable frameworks that illustrate the interconnectedness of life forms and their environments. Their study not only furthers our comprehension of ecological dynamics but also serves as a foundation for implementing practices that respect and harness the inherent wisdom of nature.
The Importance of Natural Systems in Sustainable Development
Natural System in Use play a crucial role in promoting sustainable development by ensuring environmental balance, effective resource management, and the overall well-being of communities. These systems, which encompass ecosystems, biodiversity, and natural resources, provide essential services that are vital for human survival and economic prosperity. For instance, forests, wetlands, and oceans contribute to carbon sequestration, water purification, and soil fertility, thereby supporting agricultural productivity and maintaining ecological integrity.
The integration of Natural System in Use into development plans is fundamental for creating sustainable practices. Recognizing the interconnectedness between human activities and natural ecosystems is essential; when development prioritizes short-term gains over long-term sustainability, it threatens the delicate balance of these systems. Soil degradation, deforestation, and loss of biodiversity are some of the consequences that may arise from neglecting the natural system in use. By incorporating natural systems into developmental frameworks, stakeholders can promote responsible environmental stewardship and mitigate adverse impacts on ecosystems.
Effective resource management involves not only the sustainable extraction of materials but also the consideration of the regenerative abilities of Natural System in Use. For instance, fishing quotas must align with aquatic ecosystem health to ensure fish populations remain viable. Similarly, sustainable forestry practices must be adopted to maintain forest ecosystems while providing timber and non-timber forest products. Community well-being is also enhanced when natural systems are preserved, as local populations often rely on these environments for sustenance, culture, and livelihoods.
Incorporating Natural System in Use into sustainable development initiatives ultimately fosters resilience among communities. By bolstering environmental sustainability, it creates a harmonious relationship between humanity and nature, which is essential for future generations. Climate change and resource scarcity underline the urgent need for a paradigm shift towards developments that embrace and enhance the natural system in use.
Examples of Natural Systems in Use
Natural System in Use have been increasingly recognized for their ability to enhance productivity, sustainability, and biodiversity across various sectors. In agriculture, one prominent example is permaculture, a holistic approach to land management that mimics the relationships found in natural ecosystems. This method utilizes a diverse range of plants and animals working together to create a self-sustaining environment. By focusing on soil health and biodiversity, permaculture not only improves crop yields but also minimizes the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides. The integration of natural systems in agricultural practices is proving to be a sustainable alternative for farmers worldwide.
Another significant area where Natural System in Use forestry management. The concept of agroforestry combines agriculture and forestry practices by incorporating trees alongside crops or livestock. This approach enhances biodiversity by providing habitats for various species, improving soil quality through organic matter, and reducing soil erosion. Additionally, agroforestry can aid in carbon sequestration, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts. Various regions, such as Southeast Asia and parts of Africa, have successfully employed agroforestry techniques, yielding positive environmental and economic outcomes.
Urban planning also stands to benefit from Natural System in Use, particularly through the implementation of green infrastructure. Techniques such as green roofs, rain gardens, and permeable pavements harness natural processes to manage stormwater, improve air quality, and support urban biodiversity. These systems mirror natural hydrology and provide ecosystems within urban settings, enhancing both the resilience and sustainability of cities. Cities like Philadelphia and Singapore have adopted such practices, demonstrating the effectiveness of integrating natural systems into urban development.
In conclusion, examples from agriculture, forestry, and urban planning illustrate the diverse applications of Natural System in Use. Each case highlights the potential benefits of these systems in fostering productivity while promoting sustainability and enhancing biodiversity.
Innovations and Technologies Leveraging Natural Systems
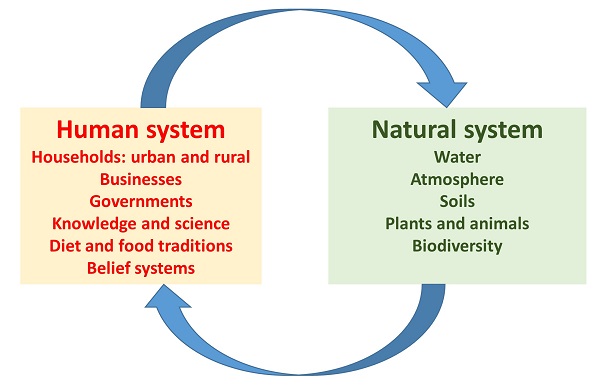
The integration of innovations and technologies embracing the concept of Natural System in Use has gained significant momentum in recent years. As environmental challenges become increasingly pressing, various fields are recognizing the value of harmonizing human technology with nature’s inherent systems. One notable approach within this paradigm is biomimicry, which seeks inspiration from nature’s designs and processes to solve human problems. By studying the efficiency of natural systems, researchers and designers can develop sustainable technologies that not only benefit humanity but also respect ecological balance.
Another critical area of innovation is eco-engineering. This discipline involves building structures and systems that mimic the functionality of natural environments, promoting conservation and sustainability. For instance, green roofs and vertical gardens draw inspiration from natural ecosystems to enhance urban spaces. By leveraging the Natural System in Use that plants use to filter air and water, eco-engineered solutions can improve city resilience and reduce urban heat islands, showcasing how technology can work in concert with nature.
Furthermore, the application of traditional ecological knowledge (TEK) is becoming a vital source of wisdom for modern ecological practices. Indigenous communities have long cultivated an understanding of Natural System in Use local environments, managing land and resources sustainably for generations. By incorporating TEK into contemporary environmental management strategies, scientists and policymakers can foster a deeper appreciation of biodiversity and the interconnections present within ecosystems. This synthesis not only promotes ecological sustainability but also enhances the effectiveness of current technological applications.
As we move forward, it is essential for innovators and technologists to continue exploring the synergies between human-made technologies and Natural System in Use. Embracing these approaches can lead to a more sustainable future, where innovations not only serve human needs but also contribute to the health and functionality of our planet’s ecosystems.
Challenges Facing Natural System in Use

The natural system in use encompasses a variety of ecosystems that are integral to maintaining biodiversity and supporting life on Earth. However, these systems are currently under significant threat due to a myriad of challenges, with climate change being one of the most pressing issues. As temperatures rise, ecosystems struggle to adapt, leading to shifts in habitat ranges and alterations in species interactions. The resulting phenomena, such as more frequent extreme weather events, further exacerbate the stress on these Natural System in Use, pushing them toward the brink of collapse.
Pollution poses another significant threat to Natural System in Use. Contaminants such as plastics, heavy metals, and chemicals poison not only the environment but also the organisms that inhabit it. This degradation leads to diminished water quality, harmful algal blooms, and a decline in the health of wildlife populations. The accumulation of hazardous waste in both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems has far-reaching implications that disrupt the balance of Natural System in Use and compromise their ability to function effectively.
Habitat destruction, driven by urbanization, agriculture, and industrial activities, further compounds the challenges faced by Natural System in Use. The fragmentation of landscapes results in isolated populations, disrupting migration patterns and breeding success. This loss of connectivity between habitats demands immediate attention, as it threatens genetic diversity and the resilience of ecosystems. Additionally, overexploitation of resources, such as deforestation, overfishing, and unsustainable agricultural practices, depletes not only the species involved but also the overall health of the Natural System in Use.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for the preservation of Natural System in Use for future generations. Without immediate and concerted efforts to combat climate change, mitigate pollution, protect habitats, and promote sustainable resource management, the consequences will be dire, affecting not just the natural world but human populations reliant on these systems as well.
Policies Supporting Natural Systems
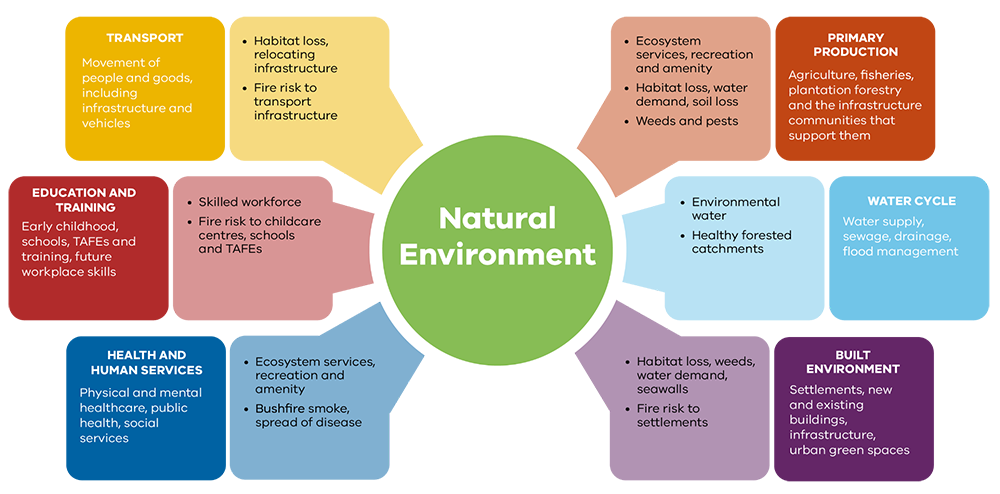
The integration of Natural System in Use effective policy frameworks is crucial for environmental sustainability. At the local, national, and international levels, various policies and legislation are designed to protect and promote these systems. One critical approach involves the establishment of conservation areas where human activity is limited to ensure the preservation of biodiversity and the ecological integrity of these systems. National governments often adopt specific policies that encourage the sustainable stewardship of natural resources, emphasizing conservation efforts that align with ecological principles.
Internationally, treaties such as the Convention on Biological Diversity and the Paris Agreement exemplify collaborative efforts aimed at enhancing Natural System in Use. These agreements aim to halt biodiversity loss and mitigate climate change, respectively, acknowledging that healthy natural systems are vital for human survival and well-being. Additionally, numerous global initiatives have been launched to promote sustainable practices, such as the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals, which address environmental challenges through an integrated approach that emphasizes the importance of protecting ecosystems.
Local community programs also play a pivotal role in supporting Natural System in Use. These initiatives often stem from grassroots movements aimed at restoring ecosystems, creating urban green spaces, or implementing sustainable land-use practices. They involve residents in the decision-making process, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility towards their environment. Such policies not only enhance the ecological resilience of natural systems but also contribute to the social and economic well-being of communities.
While many of these policies and programs have achieved significant successes, challenges remain. There are instances of insufficient funding, limited public awareness, and varying levels of political commitment that hinder efforts. Thus, continuous evaluation and adaptation of policies are necessary to address these barriers and enhance the effectiveness of initiatives aimed at supporting Natural System in Use. This dynamic process is essential for ensuring that natural resources are managed sustainably for future generations.
Case Studies of Successful Natural Systems Interventions

Successful interventions that leverage Natural System in Use provide invaluable insights into their practical application across various contexts. One notable case study is the restoration of wetlands in the Chesapeake Bay region of the United States. Faced with diminishing water quality due to urban runoff and agricultural pollution, stakeholders implemented a series of initiatives aimed at enhancing the wetlands’ natural filtration capabilities. The strategic restoration involved replanting native vegetation and re-establishing hydrological patterns disrupted by development. The outcomes were remarkable: water quality improved significantly, biodiversity increased, and the local community witnessed a resurgence in fishing and recreational activities. This case underscores the efficacy of utilizing Natural System in Use for ecological and economic revitalization.
Another compelling example can be found in the urban landscape of Melbourne, Australia, where the city implemented green infrastructure to manage stormwater. By introducing permeable surfaces and urban forests, Melbourne sought to reduce flooding while enhancing urban biodiversity. The initiatives led to a reduction of stormwater runoff by approximately 30%, along with improved urban aesthetics. The project highlighted the importance of integrating Natural System in Use within dense urban environments, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional gray infrastructure. This case illustrates the necessity of community engagement and careful planning in implementing Natural System in Use effectively.
In the agricultural sector, the adoption of agroecological practices in Brazil showcases the potential of a natural system in use. By focusing on biodiversity, soil health, and ecological balance, farmers transformed degraded landscapes into productive ecosystems. Crop rotations, intercropping, and the integration of cover crops improved soil fertility and reduced dependency on chemical fertilizers. The positive results included increased crop yields and enhanced resilience against climate change impacts. This case reflects how Natural System in Use interventions not only bolster agricultural productivity but also foster sustainable land management practices.
These case studies exemplify the diverse applications of Natural System in Use addressing environmental challenges. The lessons learned from these interventions emphasize the significance of collaboration, community involvement, and a commitment to sustainability in ensuring successful outcomes.
The Future of Natural Systems in Use

As the global community grapples with the challenges posed by climate change, biodiversity loss, and resource depletion, the future of natural systems in use takes on paramount significance. Emerging trends indicate a shift toward recognizing the intricate relationships that exist between human activities and Natural System in Use. Efforts to foster sustainability are leading to innovative approaches aimed at balancing ecological integrity with human needs.
One notable trend is the increasing integration of technology in the management of Natural System in Use. Tools such as remote sensing, data analytics, and artificial intelligence are transforming how we observe and interact with ecosystems. These advancements enable us to monitor environmental changes in real-time, facilitating informed decision-making. For instance, adaptive management techniques allow for dynamic responses to environmental shifts, ensuring that natural systems are maintained effectively and sustainably.
Moreover, an evolving understanding of the human-nature relationship will be crucial to the future of Natural System in Use. The notion of ecosystem services is gaining traction, highlighting the benefits that natural systems provide to humanity. This perspective encourages stakeholders to prioritize ecological health in policy-making and planning processes. Furthermore, grassroots movements and community-led initiatives are becoming vital, empowering local populations to take charge of their natural resources and fostering resilience against external pressures.
With these emerging trends comes a need for collaborative governance that encompasses multiple sectors, acknowledging that Natural System in Use do not operate in isolation. Engagement between scientists, policymakers, and public stakeholders will promote a holistic view necessary for sustainable management. As we move forward, continuous adaptation and foresight will be essential to navigate the intricate dynamics of natural systems, ensuring their resilience in a rapidly changing world.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In exploring the natural system in use, this article has highlighted the critical role that Natural System in Use play in ensuring sustainable practices across various domains. As we have discussed, integrating these systems into our everyday lives and industries is not merely beneficial; it is imperative for the health of our planet. Natural systems, characterized by their inherent efficiency and resilience, offer a framework for addressing environmental challenges, enhancing biodiversity, and fostering a sustainable future.
Throughout the article, we have identified how the natural system in use can support various sectors such as agriculture, urban development, and waste management. By utilizing strategies that emulate natural processes, we can reduce our ecological footprint, improve resource management, and ultimately lead to a more sustainable society. It is essential to recognize that the adoption of these practices is vital not just for environmental preservation but also for supporting economic growth and community well-being.
As stakeholders in our communities and industries, we all have a part to play in advocating for the integration of Natural System in Use. Whether you are an individual, a business owner, or a policymaker, there are steps you can take to promote these concepts. Start by educating yourself and others about the advantages of natural systems, actively participate in local sustainability initiatives, and support policies that prioritize environmental health.
We encourage readers to reflect on how they can implement the principles of Natural System in Use in their own lives and advocate for their broader application. Together, by fostering a culture of sustainability, we can ensure that natural systems flourish alongside human endeavors, ultimately contributing to a healthier planet for generations to come.






